Leveling up: master data management maturity model - the key to unlocking your data management potential
As organizations strive to improve their data management capabilities, they often turn to master data management (MDM) maturity models to help them assess their current state of master data management and identify areas for improvement.
These models provide a framework for evaluating an organization's master data management capabilities and determining its level of maturity.
A master data management maturity model is a tool that helps organizations understand their current level of capability, proficiency and effectiveness in managing and maintaining their master data.
It is a way to measure how well the organization is able to create and maintain a single, accurate and consistent view of critical business data across the company.
This involves not just managing metadata but also ensuring the integrity of data assets.
The purpose of this blog post is to introduce the master data management maturity model, explain what the organization's level of maturity means and provide some examples of how it can guide organizations in achieving a higher level of maturity in their master data management efforts.
What is the master data management maturity model?
A master data management maturity model is a framework that organizations can use to assess their current master data management capabilities and identify areas for improvement. It typically includes several levels of maturity, from initial to advanced, that organizations can use to benchmark their master data management capabilities against industry standards and best practices.
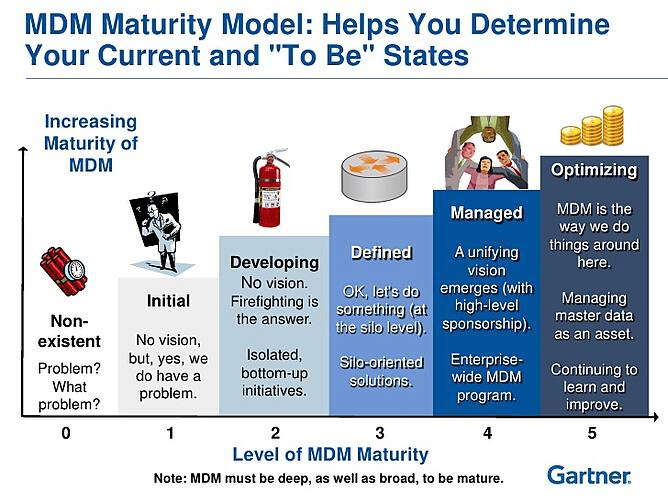
The levels of maturity in a master data management maturity model can vary depending on the framework but generally, they can be described as:
Level 1 - Initial
This level represents the starting point for master data management, where the organization has little or no master data management capabilities in place. It often involves ad hoc processes and limited use of a business glossary.
Level 2 - Developing
This level represents the implementation of basic master data management capabilities, such as data governance, data quality and data integration but they are not yet fully integrated or automated. At this level, there might be some initial steps towards metadata management and data profiling.
Level 3 - Defined
This level represents the implementation of a defined and integrated master data management program with formal processes, governance and systems in place. Organizations often start leveraging data management processes and data management strategy more effectively at this level.
Level 4 - Managed
This level represents the ability to measure and monitor the effectiveness of the MDM program, with KPIs and metrics in place to track performance and improvements are made based on the feedback. Data lifecycle management and data stewardship also become central at this level.
Level 5 - Optimizing
This level represents the ability to optimize and continuously improve the MDM program with a focus on data analytics, automation and innovation. At level 5, the organization achieves a high level of data-driven decision-making and competitive advantage through advanced business intelligence tools.
This maturity model can help organizations understand the current state of their master data management capabilities and identify areas for improvement. It also provides a roadmap for organizations to follow as they work to improve their master data management capabilities over time.
What does the level of an organization's maturity mean?
An organization's maturity level in master data management refers to the level of capability and proficiency the organization has in managing and maintaining its master data.
It is a measure of how well the organization is able to create and maintain a single, accurate and consistent view of critical business data across the company.
A low maturity level means that the organization is just starting to implement master data management and may have a limited understanding of the importance of master data and how to manage it. The organization may not have well-defined processes and procedures in place for managing master data and data quality may be poor.
A high maturity level means that the organization has a strong understanding of the importance of master data and has well-defined processes and procedures in place for managing it.
Data quality is high and the organization is able to use master data to drive business decisions and improve business processes.
An organization's maturity level can vary depending on the specific data domain or function being evaluated, as well as the size of the organization. However, it is important to note that an organization can have a high maturity level in one domain and a low maturity level in another domain.
Tools like a data catalog or a data management framework can help in standardizing and enhancing these capabilities.
How can the master data management maturity model be used?
The master data management maturity model can be used in several ways, including:
- Assessing the current state of master data management: The model can be used to assess the current state of MDM within an organization, identifying areas of strength and weakness and providing a baseline for future improvements.
- Setting goals and objectives: The model can be used to set goals and objectives for master data management and to determine the level of maturity that the organization needs to achieve in order to meet its business objectives.
- Prioritizing initiatives: The model can be used to prioritize master data management initiatives and to determine which initiatives should be implemented first based on the organization's current level of maturity. This helps in building a solid business case for each initiative.
- Measuring progress: The model can be used to measure progress over time and to determine whether the organization is on track to achieve its goals and objectives. Data architecture and data security are often critical areas to monitor.
- Identifying best practices: The model can be used to identify best practices for master data management, and to determine how these best practices can be adapted to the organization's specific needs.
- Communicating with stakeholders: The model can be used to communicate the organization's current level of maturity, goals and objectives to stakeholders and to involve them in the process of improving master data management.
- Benchmarking: The model can also be used to benchmark against other organizations in the same industry and/or same size to have a better understanding of where the company stands compared to others and to identify best practices that can be adopted.
Benefits of using a master data management maturity model
Implementing a data management maturity model offers numerous benefits to organizations of all sizes. Below is a closer look at the various advantages.
Improved data quality
Using a data maturity model helps businesses identify and resolve data quality issues. It ensures all data is accurate, consistent, and reliable, which leads to better decision-making and stronger overall business performance.
Enhanced decision-making
Reliable data can provide your business with a solid foundation for strategic planning and operational efficiency. Implementing a data maturity model gives you the competitive advantage from which to build that foundation.
Regulatory compliance
A well-implemented data management maturity model ensures that organizations adhere to industry standards and regulations. This compliance helps avoid legal issues and potential fines, while also building trust with customers and stakeholders.
More operational efficiency
Streamlined data management processes reduce redundancy and minimize errors, leading to increased efficiency in operations. This efficiency translates to cost savings and improved productivity across the organization.